During a visit to Leica in
Germany a while ago, I had the opportunity to get a personal tour of the
facilities and to ask a lot of questions.
At one point my contact person and guide introduced me to a gentleman
who was working in the lens design department.
I took the opportunity to ask a lot of questions about Leica lenses
which also led me to ask about filters.
My question was met with a very stern face with him saying,
“If we had intended our lenses to have
flat pieces of glass in front, we would have designed them that way.”
Indeed there used to be a
Leica lens that was designed to be utilized at times with a filter.
From the very beginning,
Leica lenses have always had a very high reputation for their sharpness and
their special tonal performance. This
was a prerequisite, demanded by Oskar Barnck and realized by Max Berek with
even his first lens designs for the Leica.
As a matter of fact, Leitz
had been criticized from time to time for not having any good portrait
lenses. Many Leica users thought that
the Leica lenses were often too sharp for portrait work. That gave the impetus for Max Berek to design
the Leitz Thambar at the beginning of the 1930s.

The Thambar was a soft
focus lens, displaying some rather unique characteristics, which made it one of
the premier portrait lenses of the time.
The soft focus effect was the result of the lens having been purposely designed
with a considerable amount of residual spherical aberration. The name Thambar was derived from Greek,
meaning “something that inspires wonder”, or wonderful. The lens was comprised of four elements, with
the two central elements cemented to form one group. A very similar formula was later chosen for
the 125mm Hektor for use on the Visoflex.

Leitz Thambar on a Leica
IIIc with VIDOM viewfinder
The spherical aberration
of the lens was produced primarily at the outer perimeter of the lens. Stopping it down to smaller apertures would
reduce this effect and it was totally eliminated at f/9. To further enhance the soft focus effect, the
lens came supplied with a special, clear filter that had a one centimeter
mirrored spot in the center which eliminated the sharp image created by the
center of the lens.

Element configuration of
the Thambar with installed filter on left

Leitz New York Thambar
brochure
The maximum aperture of
the lens was f/2.2. This was reduced to
f/2.3 with the center spot filter in place.
For that reason the Thambar had two aperture scales, one in white for
the f/stops without the filter and one in red for the stops with the filter
installed. The red scale went from f/2.3
to f/6.3 because above f/6.3 the filter became useless. The maximum soft focus effect was obtained
with the lens wide open and with the filter installed. Stopping the lens down would diminish this
effect, thus giving the photographer full control over the amount of soft
focus. Photographing with back lighting
or lighting that produced flare would further increase the soft focus
effect. The distance of the subject also
had a significant effect on the softness.
The Thambar actually was
relatively difficult to use because the rangefinder of the camera did not allow
the soft focus effect of the lens to be seen.
Subsequently a fair amount of experience was necessary to use the lens
effectively.
The production of the lens
started on 1935 and ended in 1949.
According to company records, about 3000 lenses were produced. Today the Thambar is one of the most sought
after pieces by Leica collectors. Even
though a production of 3000 lenses is not all that rare, it is difficult to
find complete sets with the original filter, and sets complete with the filter
and the original red boxes are quite rare.
The Thambar is indeed a legendary piece of equipment among Leica
enthusiasts.
But what about filters in
general? The camera accessory market
offers an abundance of filters that we can screw on, slide on or otherwise
attach to our lenses. Along with it
there is the never-ending discussion about their necessity. Filters certainly are not some frivolous item
that sinister accessory manufacturers have dreamed up to get their hands onto
more of our photography budgets.


For instance, there are
color correction filters. These have
lost a lot of their importance with the advent of digital photography where white
balancing has virtually eliminated their need.
But especially among Leica users, film and film cameras are still widely
used and so are color correction filters.
Anyone who has ever shot under fluorescent lighting appreciates the FLD
and FLB filters that get rid of the ugly green cast common under those lighting
conditions. We have the choice of
daylight and tungsten film, but have the wrong film in your camera, and you
will appreciate a proper color balancing filter to be able to keep on shooting
without ending up with overly red or blue images. Excessive amounts of blue also occur when
shooting during winter with snow covered ground on bright, sunny days. The blue of the sky reflecting off the snow
will generally cause an excess amount of blue, something easily corrected with
a skylight filter.
Equally important, especially to film photographers, are filters that will change the tonality of the resulting photographs, for instance a yellow, orange or red filter to darken the sky. These certainly are helpful to assure better photographs. The same is the case with polarizing filter which can eliminate reflections of surfaces that are not electrically conductive. This can often also lead to more intense colors.
Equally important, especially to film photographers, are filters that will change the tonality of the resulting photographs, for instance a yellow, orange or red filter to darken the sky. These certainly are helpful to assure better photographs. The same is the case with polarizing filter which can eliminate reflections of surfaces that are not electrically conductive. This can often also lead to more intense colors.
Then there are a myriad of
special effects filters. These do apply
to equally to film as well as digital photography. The need or value of them can only be
assessed by the individual photographer.
It’s an eye of the beholder thing.
Finally, there is the
issue of lens protection. Many
photographers have UV filters permanently attached to their lenses as a means
of protecting them in case of a mishap.
They certainly offer a certain amount of protection and the argument
that it is a lot less expensive to replace a filter than a lens does make sense
at face value.
Hearing the “If we had
intended our lenses to have flat pieces of glass in front, we would have
designed them that way” comment caused me to research the topic once I had
returned home. After all, how bad can a
flat piece of glass in front of a lens be?
Flat is the keyword here.
Unfortunately, some filters are less flat than others. Ideally, a filter is made of high quality,
optical glass and ground from a blank, just like any lens element. The only difference is that the two surfaces
have no curvature. The same precision
and tolerances should be applied as with lenses. Only that will give the assurance that the
two glass surfaces are perfectly parallel to each other.
Unfortunately that is not
always the case. For one thing, there
are two distinctly different production methods. One is the grinding process. This is an expensive process that is only
applied by the top filter manufacturers.
Unfortunately, the majority of filters are made in a much cheaper
way. Here large, flat, narrowly rimmed
surfaces are filled with glass granules and then heated to melt the glass into
a large sheet. To make the actual
filters, these glass sheets are again heated to the point where they become
pliable and the filters are stamped in a process not unlike a cookie
cutter. Cheap but not very precise. For one thing, the two glass surfaces are not
nearly as parallel as can be assured with the grinding process. Secondly, the stamping does add a
considerable amount of physical distortion to the edges of the filter which in
turn does adversely affect lens performance.
Spectral transmission is
another, important issue. Many filters
need to be made with certain colorations to assure their proper effects. Here too we find considerable differences in
accuracy. High quality filters are
always dyed in the mass, meaning the glasses which the filters are made from
receive the correct coloration during the process of making the glass. Unfortunately this process too is subject to
considerable differences in accuracy.
A much less desirable
approach is to sandwich dyed gels between two pieces of clear glass to achieve
the proper coloration. Not only are
there differences in accuracy regarding the spectral accuracy of the gels, but
the problems of parallelism of the filter surfaces are doubled. This is actually an old, outdated approach
and hardly any filter manufacturer still uses this process.
The worst of all filters
are the ones made of acrylic rather than glass.
By nature these need to be a lot thicker to assure the desired
effects. In addition, even the best acrylics
are not nearly as clear as good, optical glass, thus adding to the undesirable
effects of these less expensive alternatives.
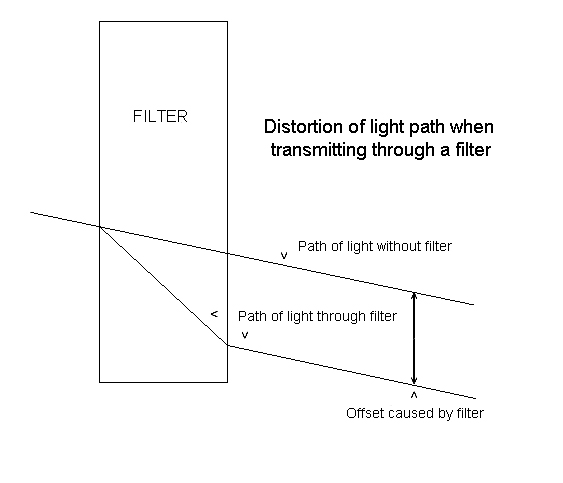
The problem lies in the
fact that when light hits the filter, it does not transmit straight through
unless the light hits the filter in a 90 degree angle. There will always be a certain offset of the
light path. The steeper the angle and
the thicker the filter, the more pronounced this is. The only filters ever made to prevent this
are curved filters. These are designed
for certain focal lengths where the curvature is such that the light path
through the glass is always reaching the filter in 90 degree angles. These filters are prohibitively expensive.
Machining of filter mounts and
finished mount, ready for anodizing
Finally, there are the
filter mounts. Needless to say, we
should stay away from plastic ones. They
simply don’t offer enough precision to be worth any consideration. Most filter mounts are made of aluminum. However, most high quality lenses also use
aluminum for the lens barrels. Aluminum
against aluminum unfortunately has a huge amount of friction. This quite easily leads to filters being very
difficult to remove. The best filter
mounts are the ones made of brass. Brass
against aluminum has a very low coefficient of friction and therefore brass
mount filters are always quite easy to remove.
This brings us back to UV
filters, permanently attached for protection.
Do we really want this, do we really need this? Based on the flat glass comment at Leitz
Wetzlar, I never use any filters unless absolutely necessary and I have done so
for years. None of my lenses have ever
been hurt because I take other safety precautions. The main one being that I always use a solid
lens shade. That gives any lens a
considerable amount of protection because the glass surface of the lens is
recessed by a certain amount. This
greatly eliminates the possibility of physical harm. Of course accidents can happen. I look at my insurance as a measure to
protect my lenses in those cases.
Of course when shooting
under condition where these measures are inadequate, a UV filter is definitely
a good idea. For instance when shooting
under extremely dusty conditions, or when wind whips up a lot of dust and fine
sand, we should not subject our lenses to such ill treatment. That is where a high quality UV filter is
definitely helpful. But personally, I
leave it at that.
Should we all use just
Leica filters? The simple answer is
no. Leica is not a filter
manufacturer. To my knowledge most of
their filters are made by Schneider through their B+W division. B+W have proven to make some of the highest
quality filters money can buy. Equal in
performance are the Heliopan filters.
Heliopan is owned by Zeiss. Staying
with those two manufacturers will always give you the assurance of keeping the
ill side effects of filters to a minimum.
The top quality filters from Hoya could be added to that category as
well.
Considering the overall
performance of Leica and other high quality lenses it just doesn’t seem right
to put flat pieces of glass in front of them except unless absolutely necessary. It especially doesn’t make any sense at all
to have the light pass through a cheaply made, low quality filter before it
even reaches the lens just to save a few bucks.
That approach has served me well over the years and will continue to do
so.

________________________________________________________________________________________
To comment or to read comments please scroll past the ads below.
All ads present items of interest to Leica owners.
To comment or to read comments please scroll past the ads below.
All ads present items of interest to Leica owners.

For rare and collectible cameras go to: http://www.tamarkin.com/leicagallery/upcoming-shows
For rare and collectible cameras go to: http://www.tamarkin.com/leicagallery/upcoming-shows
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Please make payment via PayPal to GMP Photography
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Please make payment via PayPal to GMP Photography
Click on image to enlarge
Order: info@gmpphoto.com
Please make payment via PayPal to GMP Photography














No comments:
Post a Comment